Scientists find evidence for warm liquid water ocean under Enceladus
Posted: Thu, Mar 12, 2015, 10:56 PM ET (0256 GMT)
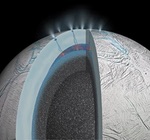 Any icy moon of Saturn likely has a warm ocean of liquid water beneath its surface, scientists reported this week. In a paper published in the journal Nature, scientists concluded that a particular type of dust grain found in one of Saturn's rings originated from within Enceladus, the result of a kind of chemical reaction between rock and water that requires temperatures of at least 90 degrees Celsius. Those dust grains were ejected from the moon via geysers. Scientists said this hydrothermal activity is the best evidence to date that Enceladus has a subsurface of liquid water and could be hospitable to life. A second paper, published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, linked an excess of methane found in the moon's plumes to processes within that liquid water ocean.
Any icy moon of Saturn likely has a warm ocean of liquid water beneath its surface, scientists reported this week. In a paper published in the journal Nature, scientists concluded that a particular type of dust grain found in one of Saturn's rings originated from within Enceladus, the result of a kind of chemical reaction between rock and water that requires temperatures of at least 90 degrees Celsius. Those dust grains were ejected from the moon via geysers. Scientists said this hydrothermal activity is the best evidence to date that Enceladus has a subsurface of liquid water and could be hospitable to life. A second paper, published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, linked an excess of methane found in the moon's plumes to processes within that liquid water ocean.
 Any icy moon of Saturn likely has a warm ocean of liquid water beneath its surface, scientists reported this week. In a paper published in the journal Nature, scientists concluded that a particular type of dust grain found in one of Saturn's rings originated from within Enceladus, the result of a kind of chemical reaction between rock and water that requires temperatures of at least 90 degrees Celsius. Those dust grains were ejected from the moon via geysers. Scientists said this hydrothermal activity is the best evidence to date that Enceladus has a subsurface of liquid water and could be hospitable to life. A second paper, published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, linked an excess of methane found in the moon's plumes to processes within that liquid water ocean.
Any icy moon of Saturn likely has a warm ocean of liquid water beneath its surface, scientists reported this week. In a paper published in the journal Nature, scientists concluded that a particular type of dust grain found in one of Saturn's rings originated from within Enceladus, the result of a kind of chemical reaction between rock and water that requires temperatures of at least 90 degrees Celsius. Those dust grains were ejected from the moon via geysers. Scientists said this hydrothermal activity is the best evidence to date that Enceladus has a subsurface of liquid water and could be hospitable to life. A second paper, published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, linked an excess of methane found in the moon's plumes to processes within that liquid water ocean.
Related Links:
| <<previous article | next article>> |
|
news in brief
|
|
NASA releases report on Starliner crewed test flight problems
Posted: Sun, Feb 22 11:45 AM ET (1645 GMT) |
|
news links
|
|
Monday, February 23
The space race is being rewritten by AI – and Europe risks falling behind
EU-Startups — 5:38 am ET (1038 GMT) Space Solar Power Will Inevitably Trump Trump’s War On Solar Power
CleanTechnica — 5:34 am ET (1034 GMT) Foushee outlines space policy at Duke amid competitive primary election
Duke Univ. Chronicle — 5:32 am ET (1032 GMT) How the free market can free NASA from the Space Launch System
The Hill — 5:28 am ET (1028 GMT) ESA Awards Contracts for Lunar Remote Camp Studies
European Spaceflight — 5:26 am ET (1026 GMT) |