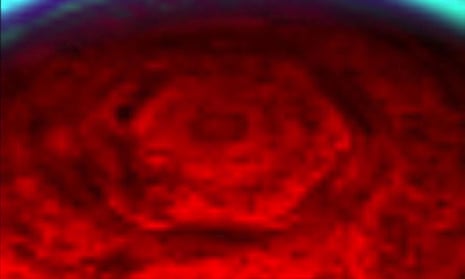
Nasa scientists are investigating why the six-sided jet stream at Saturn’s north pole has changed colour over the past four years.
When the region, which is known as the hexagon, was photographed by the Cassini wide-angle camera in 2012 it appeared to be blue. But when the spacecraft passed over it again in 2016 it seemed to have changed to gold.
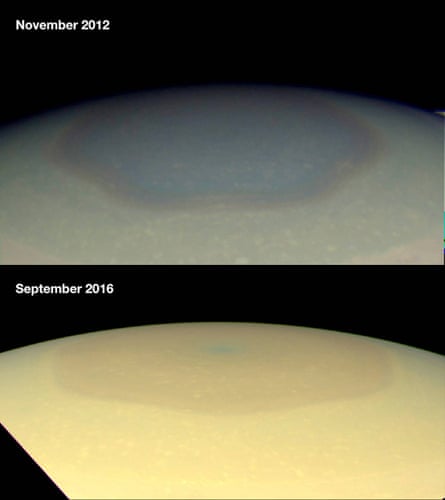

Nasa said its researchers were examining the phenomenon and believed it could be related to Saturn’s seasons and the length of its years – which are equal to 29 Earth years.
“In particular the change from a bluish colour to a more golden hue may be due to the increased production of photochemical hazes in the atmosphere as the north pole approaches summer solstice in May 2017,” the space agency said on its website.
“During the polar winter night between November 1995 and August 2009, Saturn’s north polar atmosphere became clear of aerosols produced by photochemical reactions – reactions involving sunlight and the atmosphere.
“Since the planet experienced equinox in August 2009, the polar atmosphere has been basking in continuous sunshine and aerosols are being produced inside of the hexagon, around the north pole, making the polar atmosphere appear hazy today.”
Cassini began its primary mission in 2004, having been launched in 1997, to undertake a close-up study of the sixth planet from the sun and its moons.